Image 1 of 2
Image 1 of 2

 Image 2 of 2
Image 2 of 2



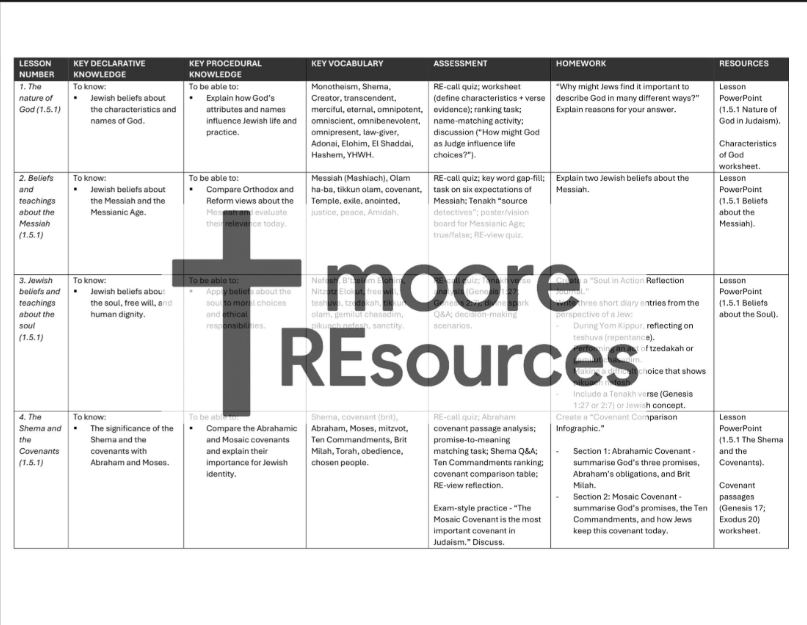
1.51 Key Beliefs and Teachings in Judaism
Introduce students to the core theological foundations of Judaism with this full-coverage Lesson Pack for 1.5.1d: Key Beliefs and Teachings in Judaism. This resource helps students gain a clear, structured understanding of Jewish beliefs about God, the soul, the Messiah, and sacred texts — including the significance of covenants and denominational differences — all aligned with the WJEC 2025 specification.
Learners Will Understand:
Nature of God in Judaism
Creator ex nihilo (Genesis 1:1–12)
Attributes of God:
One (monotheism)
Transcendent (Isaiah 55:8–9)
Merciful, Eternal, Judge, Law-giver
Omnipotent, Omniscient, Omnibenevolent, *Omnipresent
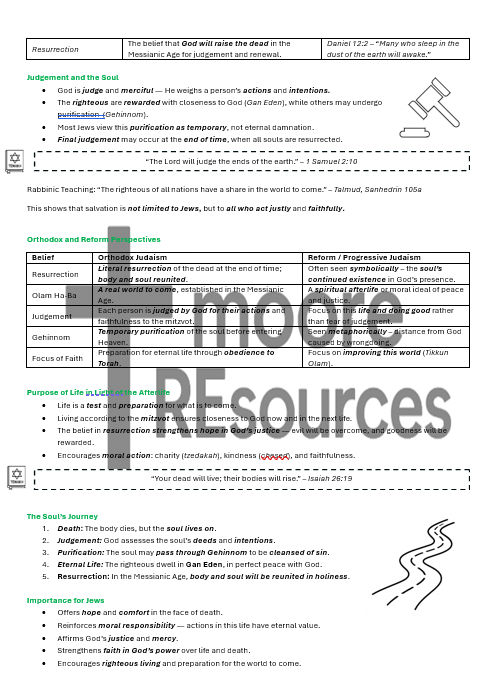
The Messiah and the Messianic Age
The expectations of the Messiah
A future Messianic Age of peace and knowledge (Isaiah 11:9)
Orthodox and Reform views of the Messiah and Messianic Age
Connection to Olam Ha-Ba (the World to Come)
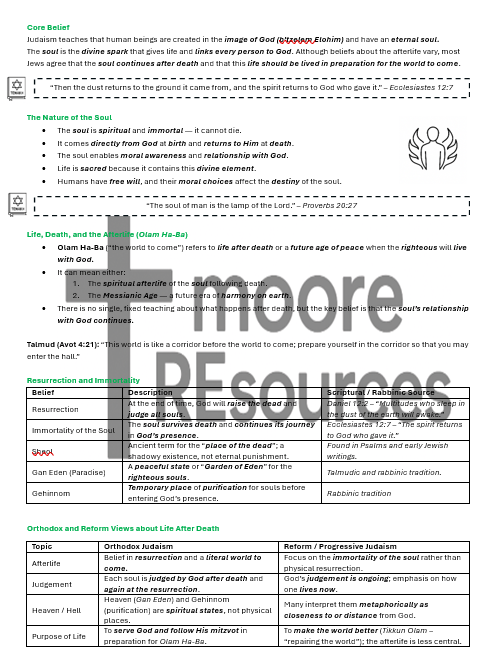
Beliefs About the Soul
Created in the image of God and presence of a divine spark from God (Genesis 2:7)
The soul is eternal, transcendent, and humans possess rationality and free will
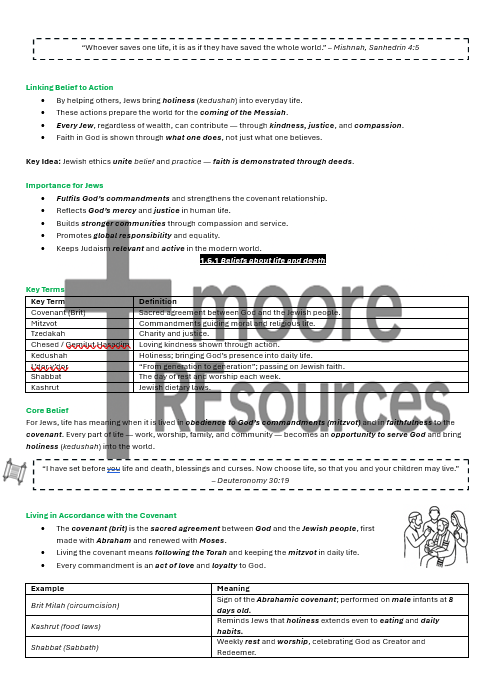
Key Beliefs and Sacred Teachings
The Shema (Deuteronomy 6:4–5) – central statement of monotheism and love for God
Covenants:
Abrahamic and Mosaic Covenants
Importance of covenants for Jewish life today
Sacred Texts in Jewish Life
Roles of the Torah, Tenakh, and Talmud
Different interpretations in Orthodox and Reform Judaism
Use of sacred texts in daily worship, study, and decision-making
Suitable for:
WJEC GCSE Religious Studies (from 2025)
KS4 Judaism units or interfaith topics
Theology, Philosophy, and Ethics crossover content
Revision, homework, and cover lessons
Introduce students to the core theological foundations of Judaism with this full-coverage Lesson Pack for 1.5.1d: Key Beliefs and Teachings in Judaism. This resource helps students gain a clear, structured understanding of Jewish beliefs about God, the soul, the Messiah, and sacred texts — including the significance of covenants and denominational differences — all aligned with the WJEC 2025 specification.
Learners Will Understand:
Nature of God in Judaism
Creator ex nihilo (Genesis 1:1–12)
Attributes of God:
One (monotheism)
Transcendent (Isaiah 55:8–9)
Merciful, Eternal, Judge, Law-giver
Omnipotent, Omniscient, Omnibenevolent, *Omnipresent
The Messiah and the Messianic Age
The expectations of the Messiah
A future Messianic Age of peace and knowledge (Isaiah 11:9)
Orthodox and Reform views of the Messiah and Messianic Age
Connection to Olam Ha-Ba (the World to Come)
Beliefs About the Soul
Created in the image of God and presence of a divine spark from God (Genesis 2:7)
The soul is eternal, transcendent, and humans possess rationality and free will
Key Beliefs and Sacred Teachings
The Shema (Deuteronomy 6:4–5) – central statement of monotheism and love for God
Covenants:
Abrahamic and Mosaic Covenants
Importance of covenants for Jewish life today
Sacred Texts in Jewish Life
Roles of the Torah, Tenakh, and Talmud
Different interpretations in Orthodox and Reform Judaism
Use of sacred texts in daily worship, study, and decision-making
Suitable for:
WJEC GCSE Religious Studies (from 2025)
KS4 Judaism units or interfaith topics
Theology, Philosophy, and Ethics crossover content
Revision, homework, and cover lessons